enzymatic gravimetric method total dietary fiber|total dietary fiber method : bespoke A method for the determination of insoluble (IDF), soluble (SDF), and total dietary fiber (TDF), as defined by the CODEX Alimentarius, was validated in foods. Resultado da Motos: R$ 25,00. Motorhome R$65,00. VIP para carros: R$55,00. Valores válidos até 20/11/2017." há mais de um ano. Avaliou esta atração. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da A través de tu Negocio Amway™, puedes ofrecer un amplio portafolio de productos de alta calidad. Al vender estos productos a tus clientes puedes ganar dinero y .
A method for the determination of insoluble (IDF), soluble (SDF), and total dietary fiber (TDF), as defined by the CODEX Alimentarius, was validated in foods.In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37C to .A simple, accurate, and reliable method for the measurement of total dietary fiber .Based upon the principles of AOAC Official Methods 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates water-insoluble and water-soluble dietary fiber. This method extends the .
total dietary fiber method
total dietary fiber
In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37C to simulate human intestinal digestion followed by gravimetric isolation and quantitation of . Since 1989, total dietary fiber values in USDA databases were determined by the enzymatic-gravimetric (EGF) method (AOAC 991.43), where “fiber” is the residue remaining .
A simple, accurate, and reliable method for the measurement of total dietary fiber (TDF) according to the Codex definition (2009) was developed and successfully .
For total dietary fiber (TDF), enzyme digestate is treated with alcohol to precipitate soluble dietary fiber before filtering, and T DF residue is washed with alcohol and acetone,.
Enzymes employed had to meet specific activity requirements and be devoid of contaminating enzymes active on dietary fibre components. The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in .A method is described for the measurement of insoluble, soluble, and total dietary fiber (IDF, SDF, and TDF, respectively), inclusive of the resistant starch (RS) and the water:alcohol .A method for measurement of total dietary fiber (TDF) has been validated. This method is applicable to plant materials, foods, and food ingredients as consumed, consistent with the .
In the early 1980s, a enzymatic-gravimetric method was developed in which the sum of soluble and insoluble polysaccharides and lignin were measured as a unit and considered to be total .
The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in Foods; Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method’ 4, 5. Subsequently, the method was extended to allow measurement of total, soluble and insoluble . Abstract. A broad range of AOAC Official Methods of Analysis SM (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since the adoption of the Prosky method (OMA 985.29). OMA 985.29 and other OMA were developed to support the Trowell definition of DF. However, these methods do not measure .A method for the determination of total dietary fiber (TDF), as defined by the CODEX Alimentarius, was validated in foods. Based upon the principles of AOAC Official Methods 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, re . Since 1989, total dietary fiber values in USDA databases were determined by the enzymatic-gravimetric (EGF) method (AOAC 991.43), where “fiber” is the residue remaining after samples are subjected to enzymatic treatments mimicking digestion.
In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37C to simulate human intestinal digestion followed by gravimetric isolation and quantitation of HMWDF and the use of LC to quantitate low-molecular-weight soluble dietary fiber (LMWSDF). The method thus quantitates the complete range of dietary fiber components from .This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Definition 2009, including naturally occurring, isolated, modified, and synthetic polymers .Two general types of methods have been developed for isolating and analyzing dietary fiber: enzymatic-gravimetric and enzymatic-chemical. The food components isolated vary depending on the method used. Both the enzymatic-gravimetric and enzymatic-chemical methods have undergone a number of modifications and improvements, most occurring over the last 20 .
32-06.01 Total Dietary Fiber—Rapid Gravimetric Method. . The value obtained from this polydextrose assay may be added to the values from the enzyme-gravimetric methods without concern for double counting. Polydextrose is extracted from food with hot water and centrifuged. The supernatant then passes through a centrifugal ultrafilter to .
Determination of Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Dietary Fiber in Foods—Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method, MES-TRIS Buffer: Collaborative Study Sungsoo C Lee, Sungsoo C Lee Kellogg Company, PO Box 3423, Battle Creek, MI 49016. . collaborative study of methods for the determination of soluble, insoluble, and total dietary fiber (SDF, .Consuming a diet high in dietary fiber offers health benefits. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration states that eating a diet high in dietary fiber promotes healthy bowel function and that a diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and grain products containing dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, and is low in saturated fat and cholesterol may reduce the risk of heart disease.
Enzymatic-gravimetric method for the determination of Total Dietary Fiber in foods. Contents of package and storage a-Amylase solution 5 ml Protease solution 5 ml Amyloglucosidase solution 3 × 5 ml Store the reagents at +2 to +8°C. General The term “Total Dietary Fiber” covers a large number of complex organic compounds, essentially veg-
Two methods (an AOAC and a simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method) were used to analyze seven types of canned legumes and eight cooked legumes. Total dietary fiber (TDF) of the canned products ranged between 17% and 23% (dry basis) for chick peas, McCleary BV, DeVries JW, Rader JI, Cohen G, Prosky L, Mugford DC, Champ M, Okuma K: Determination of total dietary fiber (CODEX definition) by enzymatic-gravimetric method and liquid chromatography: collaborative study. J AOAC Int. 2010, 93: 221-33. CAS PubMed Google Scholar OMA 2022.01 is a robust and reproducible method for the analysis of insoluble, soluble (SDFP and SDFS), and TDF in a wide range of matrixes. . Determination of Insoluble, Soluble, and Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Using a Rapid Integrated Procedure of Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatography: First Action 2022.01 J AOAC Int. 2022 .This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant material, foods, and food .
Insoluble Dietary Fibre in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method and Food Products AOAC 991.42 Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method Deitary Fibre in Foods AOAC 991.43 AOAC 985.29 Total Dietary Fibre in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method AOAC 993.19 Enzymatic-Gravimetric MethodSoluble Dietary Fibre in Food and Food Products Enzymatic–gravimetric methods have been recommended to determine dietary fiber. Recently in Brazil, the method 985.29 of AOAC (1990) was adopted for fiber levels notification on the label of packed food products (Brasil, 1998).Several problems as to the performance of these modifications of the method have been recorded (Jeraci and Van Soest, . Analysis of total dietary fiber (TDF) is an expensive method due to the use of enzymes. The present study compared the measured TDF content in dry fruits using two methods (enzymatic gravimetric method with and without enzymes α-amylase, protease and amyloglucosidase) to validate the cost-effective non-enzymatic analysis for TDF measurement.method for measurement of total dietary fiber (AOAC Method 2009.01/AACCI method 32-45.01) was developed and adopted. Evaluation of this method over the past 8 years identified some aspects of the method that could . enzymatic/gravimetric methods and the official status of each is summarised in Table 1 and acronyms are listed in Table 2. Figure 1.
AOAC Official Method 2009.01 Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method First Action 2009 [Applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Definition 2008 (ALINORM 09/32/26), including naturally occurring, isolated, modified, and synthetic polymers meeting that definition.] This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant .Two methods (an AOAC and a simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method) were used to analyze seven types of canned legumes and eight cooked legumes. Total dietary fiber (TDF) of the canned products ranged between 17% and 23% (dry basis) for chick peas, Great Northern beans, kidney beans, pinto beans, pork & beans, vegetarian beans in tomato sauce . A broad range of AOAC official methods of analysis (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since the adoption of the Prosky method (OMA .
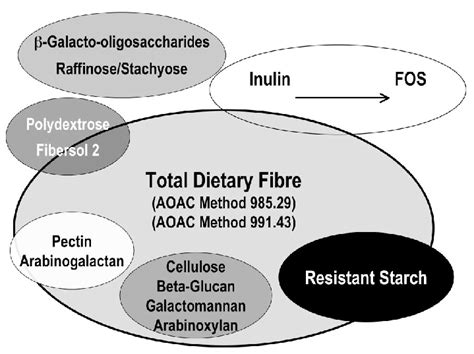
(a) Dietary fiber derived from a plant origin may include fractions of lignin and/or other compounds when associated with polysaccharides in the plant cell walls and if these compounds are quantified by the AOAC gravimetric analytical method for dietary fiber analysis; e.g., fractions of lignin and the other compounds (proteic fractions, phenolicA collaborative study was conducted on an enzymatic-gravimetric method for determination of total dietary fiber in foods, in which soluble fiber and insoluble fiber are determined separately. Ten collaborators analyzed blind duplicate test samples .
A collaborative study was conducted to determine the total dietary fiber (TDF) content of food and food products, using a combination of enzymatic and gravimetric procedures. The method was basically the same as published earlier (J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. (1984) 67, 1044-1052), with changes in the .DOI: 10.1093/JAOAC/75.3.395 Corpus ID: 128658872; Determination of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fiber in foods: enzymatic-gravimetric method, MES-TRIS buffer: collaborative study
webRoblox is the ultimate virtual universe that lets you create, share experiences with friends, and be anything you can imagine. Join millions of people and discover an infinite variety of immersive experiences created by a global community! Roblox is ushering in the next generation of entertainment. Imagine, create, and play together with .
enzymatic gravimetric method total dietary fiber|total dietary fiber method